Scoring Systems
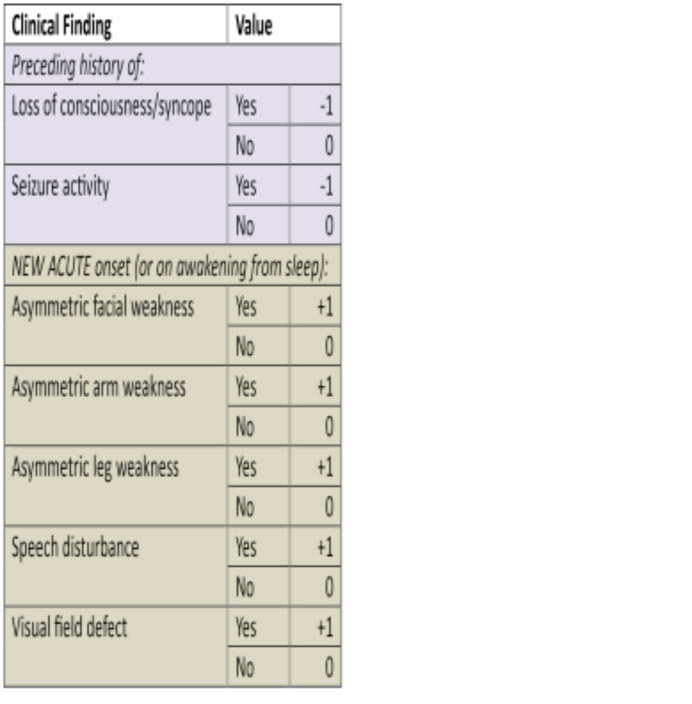
ROSIER Scale
The Recognition of Stroke in the Emergency Room (ROSIER) scale was developed to help in the initial differentiation of acute stroke from stroke mimics in the ED [10].
Table 1: ROSIER Scale
A score of zero or higher showed a sensitivity of 93% and specificity of 83% in prospective validation studies in predicting stroke.
The Canadian TIA Score
The Canadian TIA Score stratifies patients seven day risk for stroke, with or without carotid endarterectomy/carotid artery stenting.
Table 2: Canadian TIA Score

The Canadian TIA score showed an increasing risk with a higher score and when grouped into three risk bands did differentiate into risk groups.
- Score -3-3. Low risk.
- Score 4-8. Medium risk.
- Score 9-14. High risk.
These bandings seem reasonable in terms of risk assessments that might link to clinical strategies relating to discharge or rapid interventions for patients. Low risk being suitable for discharge, but high risk requiring a very rapid intervention to prevent an early stroke
The ABCD scores were unable to identify a low (<1%) risk group and thus the Canadian TIA score appears to have a significant advantage.
The derivation and validation studies for Canadian TIA score appear robust and it appears to offer advantages over our current scores[19].